Apy Vs Apr: Understanding The Key Differences And Their Impact On Your Finances
When it comes to managing your finances, understanding the terms APY (Annual Percentage Yield) and APR (Annual Percentage Rate) is crucial. These two metrics play a significant role in determining how much you earn on savings or pay on loans. Knowing the difference between APY and APR can help you make informed financial decisions that align with your goals.
In this article, we will delve deep into the definitions of APY and APR, explore their differences, and discuss their implications on various financial products. Whether you are a seasoned investor or new to personal finance, grasping these concepts can empower you to maximize your savings and minimize your costs.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of APY and APR, enabling you to navigate the financial landscape more effectively. So, let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- 1. Definition of APY and APR
- 2. How APY and APR are Calculated
- 3. Key Differences Between APY and APR
- 4. The Impact of APY and APR on Your Finances
- 5. When to Use APY vs APR
- 6. Real-World Examples of APY and APR
- 7. Choosing Between APY and APR: What You Need to Know
- 8. Conclusion
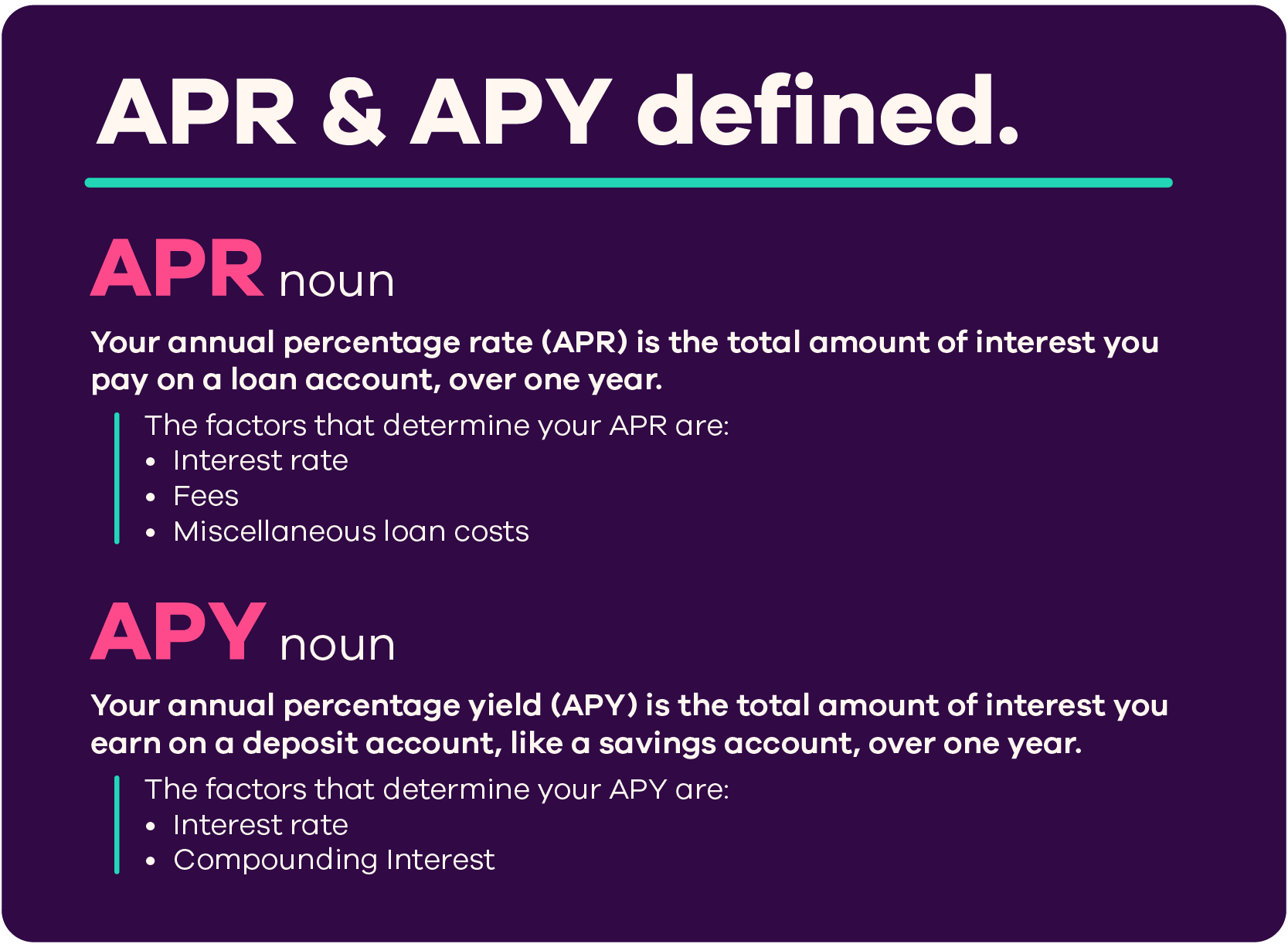
1. Definition of APY and APR
APY, or Annual Percentage Yield, represents the total amount of interest earned on an investment over a year, taking into account the effects of compounding. Essentially, it reflects the actual return on an investment, allowing you to compare different savings accounts and investment options effectively.
APR, or Annual Percentage Rate, is a broader measure that reflects the cost of borrowing. It includes the interest rate plus any additional fees or costs involved in securing a loan. Unlike APY, APR does not factor in compounding, making it a straightforward way to understand how much you will owe annually.
2. How APY and APR are Calculated
Understanding how APY and APR are calculated can provide clarity on how these rates impact your finances.
Calculating APY
APY is calculated using the formula:
APY = (1 + (r/n))^n - 1
Where:
- r = nominal interest rate (annual)
- n = number of compounding periods per year
Calculating APR
APR is calculated using the formula:
APR = (Interest + Fees) / Principal
This formula helps borrowers understand the total cost of a loan and allows for better comparisons between different loan offers.
3. Key Differences Between APY and APR
There are several significant differences between APY and APR that can influence your financial decisions:
- Purpose: APY is primarily used for savings accounts, while APR is used for loans and credit.
- Compounding: APY considers the effects of compounding, whereas APR does not.
- Representation: APY shows how much you will earn on your savings, while APR shows how much you will pay on your loans.
4. The Impact of APY and APR on Your Finances
The choice between APY and APR can significantly affect your financial outcomes. A higher APY on a savings account means more interest earned, while a lower APR on a loan means less paid in interest over time. Here are some key impacts:
- Savings Growth: Choosing an account with a higher APY can lead to substantial growth in your savings.
- Loan Costs: A lower APR can result in significant savings on interest payments for loans.
5. When to Use APY vs APR
Understanding when to look at APY versus APR can help you make better financial choices:
- Use APY: When comparing savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), or investment options.
- Use APR: When evaluating loans, mortgages, or credit cards to understand the total cost of borrowing.
6. Real-World Examples of APY and APR
Let’s explore some real-world examples to illustrate the differences between APY and APR:
- Savings Account: If a bank offers a savings account with a 2% APY, you will earn $200 on a $10,000 deposit after one year.
- Loan: If a lender offers a personal loan with a 10% APR and a loan amount of $5,000, you will pay $500 in interest over one year, excluding any fees.
7. Choosing Between APY and APR: What You Need to Know
When faced with a financial decision, understanding the nuances of APY and APR can guide you toward the best options:
- For Savings: Look for accounts with the highest APY to maximize your earnings.
- For Borrowing: Choose loans with the lowest APR to minimize interest costs.
8. Conclusion
In summary, understanding APY and APR is vital for making informed financial decisions. While APY indicates how much you can earn on savings, APR reflects the cost of borrowing. By knowing the differences and knowing when to use each, you can enhance your financial strategies and achieve your financial goals.
We encourage you to leave a comment below, share this article with others, or explore more resources on our site to further enhance your financial literacy!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back for more insightful articles that can help you navigate the world of finance.
Understanding CRSR: The Future Of Cryptocurrency Regulation
The Ultimate Guide To DJI Average: Understanding The Average In Drone Technology
Understanding The Role Of A Lawyer: Expertise, Authority, And Trustworthiness In Legal Matters
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Apr-apy-bank-hopes-cant-tell-difference_final-15cefe4dc77a4d81a02be1e2a26a4fac.png)