Understanding Reverse Stock Split: A Comprehensive Guide
Reverse stock split is a financial maneuver that can significantly impact investors and companies alike. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of reverse stock splits, exploring their purpose, benefits, and implications. Understanding this concept is crucial for any investor looking to navigate the complexities of the stock market. With the right information, you can make informed decisions that can positively affect your investment portfolio.
As the stock market evolves, companies occasionally implement strategies to enhance their stock performance and market perception. One such strategy is the reverse stock split, which may seem counterintuitive at first glance. However, it serves specific purposes that can benefit both the company and its shareholders. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of what a reverse stock split entails and its significance in the world of finance.
This guide aims to provide valuable insights into reverse stock splits, including their mechanics, advantages, and potential risks. Whether you are a seasoned investor or a newcomer to the stock market, grasping the concept of reverse stock splits can equip you with the knowledge necessary to make sound investment decisions.
Table of Contents
- What is a Reverse Stock Split?
- How Reverse Stock Split Works
- Reasons for Implementing a Reverse Stock Split
- Benefits of Reverse Stock Split
- Potential Risks of Reverse Stock Split
- Impact on Investors
- Case Studies of Reverse Stock Splits
- Conclusion
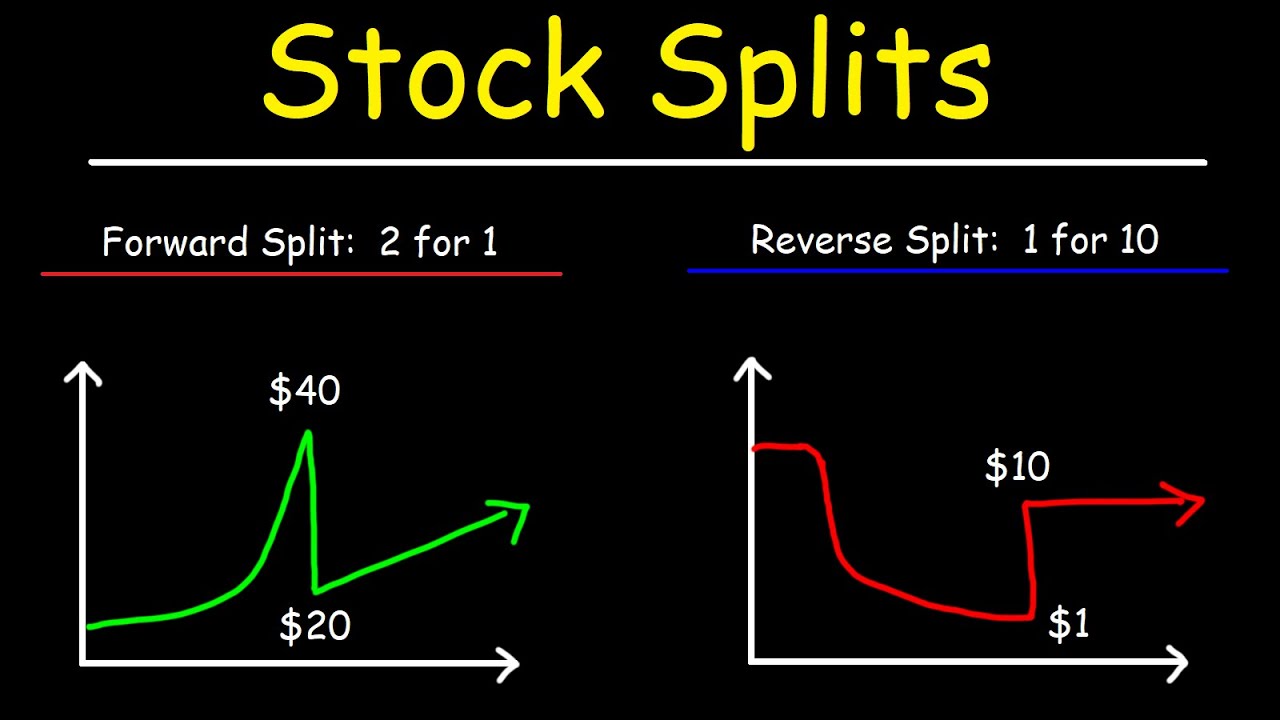
What is a Reverse Stock Split?
A reverse stock split is a corporate action in which a company reduces the number of its outstanding shares, resulting in an increase in the share price. For instance, in a 1-for-10 reverse stock split, a shareholder who holds 10 shares of a company will now own 1 share, but the value of that share will be ten times higher than before. This process does not affect the overall market capitalization of the company.
Reverse stock splits are often performed to meet minimum share price requirements set by stock exchanges, such as the Nasdaq or NYSE. Companies with low stock prices may face delisting, and a reverse stock split can help them avoid this outcome.
How Reverse Stock Split Works
Understanding the technical aspects of how a reverse stock split works is essential for investors. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- The company’s board of directors approves the reverse stock split.
- A specific ratio is determined (e.g., 1-for-5, 1-for-10).
- The company notifies shareholders and the stock exchange of the action.
- When the split is executed, shareholders receive new shares based on the agreed ratio.
- The share price adjusts accordingly, reflecting the reduced number of shares outstanding.
Example of Reverse Stock Split
Let’s illustrate this with a simple example:
- Company XYZ has 1,000,000 shares outstanding at $1 per share.
- After a 1-for-10 reverse stock split, there will be 100,000 shares outstanding.
- The new share price will be approximately $10.
Reasons for Implementing a Reverse Stock Split
Companies may choose to execute a reverse stock split for several reasons, including:
- **Avoiding Delisting:** Companies often use reverse stock splits to meet the minimum share price requirements of stock exchanges.
- **Enhancing Market Perception:** A higher stock price can improve investor perception and attract institutional investors.
- **Reducing Volatility:** By consolidating shares, companies may aim to reduce stock price volatility.
Benefits of Reverse Stock Split
The implementation of a reverse stock split can yield various benefits for companies:
- **Improved Stock Price:** A higher stock price can reduce the likelihood of being viewed as a penny stock.
- **Attracting Institutional Investors:** Many institutional investors have policies against investing in stocks below a certain price, so a reverse split can make shares more appealing.
- **Increased Trading Liquidity:** A higher stock price can lead to increased trading volume and liquidity.
Potential Risks of Reverse Stock Split
While reverse stock splits can offer benefits, there are also potential risks to consider:
- **Market Perception:** Investors may view a reverse stock split as a sign of weakness, leading to negative sentiment.
- **Volatility in Share Price:** The adjustment in the stock price can lead to increased volatility and uncertainty.
- **Loss of Investor Confidence:** Frequent reverse splits may erode trust in the company’s management and financial health.
Impact on Investors
For investors, the impact of a reverse stock split can vary. Here are some key considerations:
- **Ownership Percentage:** A reverse stock split does not change the ownership percentage of shareholders, but it alters the number of shares they hold.
- **Investment Strategy:** Investors should assess how a reverse stock split fits into their overall investment strategy and risk tolerance.
- **Monitoring Company Performance:** Post-split performance should be monitored closely to evaluate the long-term effects of the corporate action.
Case Studies of Reverse Stock Splits
Several notable companies have undergone reverse stock splits in recent years. Here are a few examples:
- **General Electric (GE):** In 2021, GE executed a 1-for-8 reverse stock split to improve its market perception following years of declining stock prices.
- **Citigroup:** In 2011, Citigroup conducted a 1-for-10 reverse stock split to stabilize its share price after experiencing significant losses during the financial crisis.
Conclusion
In summary, reverse stock splits are strategic decisions made by companies to enhance their market standing and avoid potential delisting. While they can provide benefits such as improved stock prices and increased attractiveness to institutional investors, they also come with inherent risks. Investors must stay informed and assess the implications of these corporate actions on their portfolios.
As you navigate the complexities of the stock market, understanding reverse stock splits can equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed investment choices. If you found this article valuable, consider leaving a comment or sharing it with fellow investors. For more insights and information, feel free to explore other articles on our site.
We hope to see you back for more financial insights and investment strategies!
Understanding Goff Stats: A Comprehensive Guide
Rocky Aur Rani: A Cinematic Journey Through Love And Culture
Understanding Alk: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Importance And Applications